Measuring distance in space
Posted: Oct 13, 2020
Categories: physics
This post aims to find out: How do we measure the distance from Earth to the Sun, Planets and Stars?
Let's start with a simpler question: how do we measure the distance from the ground to a tree's top?
Short answer: Triangulation.
Long answer:
In geometry, if we know two angles and one side of a triangle, we can calculate all sides of it.
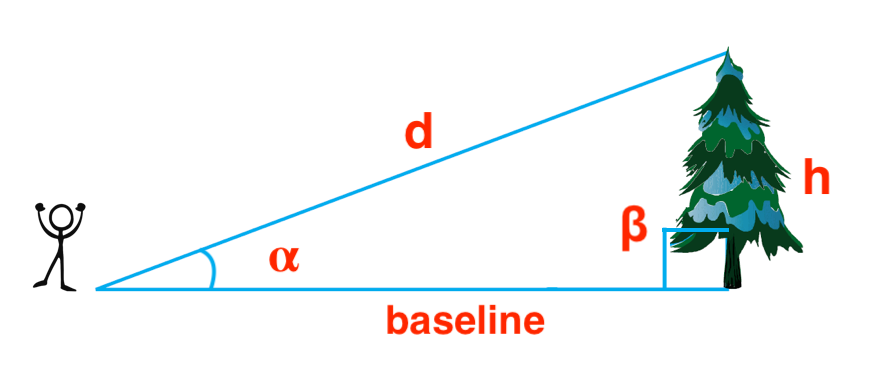
For example: consider the tree's top, root, and our position as three vertices of a triangle.
In this set up we have
With those, we can find the distance from us to the top using geometry:
This process is called triangulation and it is the basic concept for us to measure the distance to planets and stars.
Our eyes
Triangulation is interesting; it is basically how our eyes perceive the distance to objects or the depth in our 3-D space. The two eyes and object form a triangle, and with thousands generations of evolution, we've trained ourselves to precisely estimate the angles from our eyes to an object and the distance between two eyes (again, we call it the baseline).
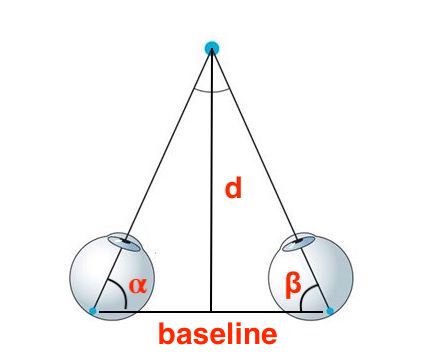
With that, our brain can estimate the distance to object using triangulation.
Earth to the Moon
We used the same technique to measure the distance to the Moon. Two telescopes are placed at two different places on earth that are as farther from each other as possible.
Then carefully measure the angles at which 2 telescopes look at the Moon; we can calculate that the Moon is 400 thousand km away.
Earth to the Sun
Unfortunately, the same technique is failed to measure the distance to the Sun. The problem is accuracy; Earth's distance to the Sun is 11500 times greater than our baseline - Earth's diameter. The baseline is too small compared to the distance, thus we can't measure the angles from 2 telescopes to the Sun as precise.
Instead, we find a near by planet that we can measure distance using triangulation. Observe its orbits to find out the relative distances between Earth to that planet and that planet to the Sun.
For example, Venus is one of the 2 planets stand between Earth and the Sun. Also, it's closer enough for us to use triangulation to measure distance, which is about 41 million km from us.
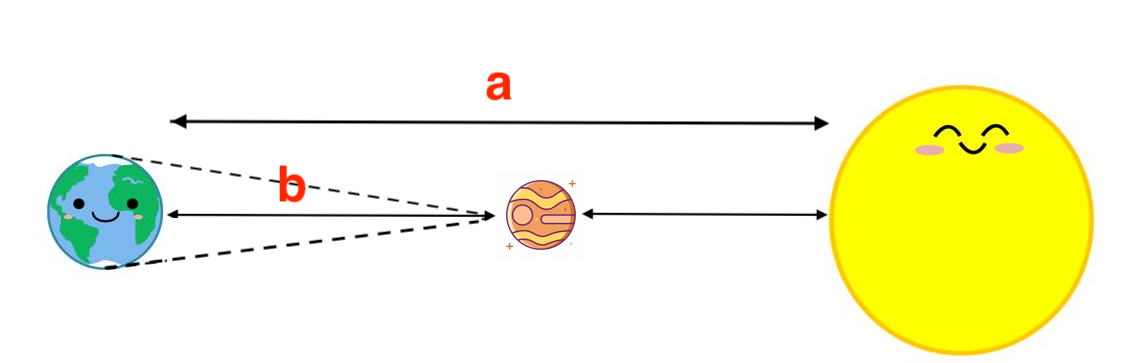
Then by observing the orbits of Earth, Venus, and Sun - which we have been doing for a long time. We found the relative distance between Earth to Sun and Earth to Venus :
That's how we find out the distance from Earth to Sun is approximately 150 million km. This distance has a unique name: astronomical unit or AU, it is usually used to measure distances within our Solar System.
The same technique is applied to calculate the distance to planets in our solar system.
Beyond our solar system
How about stars that much farther we can't find the relative distances?
Fortunately, we can go back to our triangulation because now we have the distance from Earth to the Sun. Leveraging the fact that Earth orbits around the Sun, its orbit creates an eclipse with a diameter of 300 million km. This gives us a large baseline to work with.
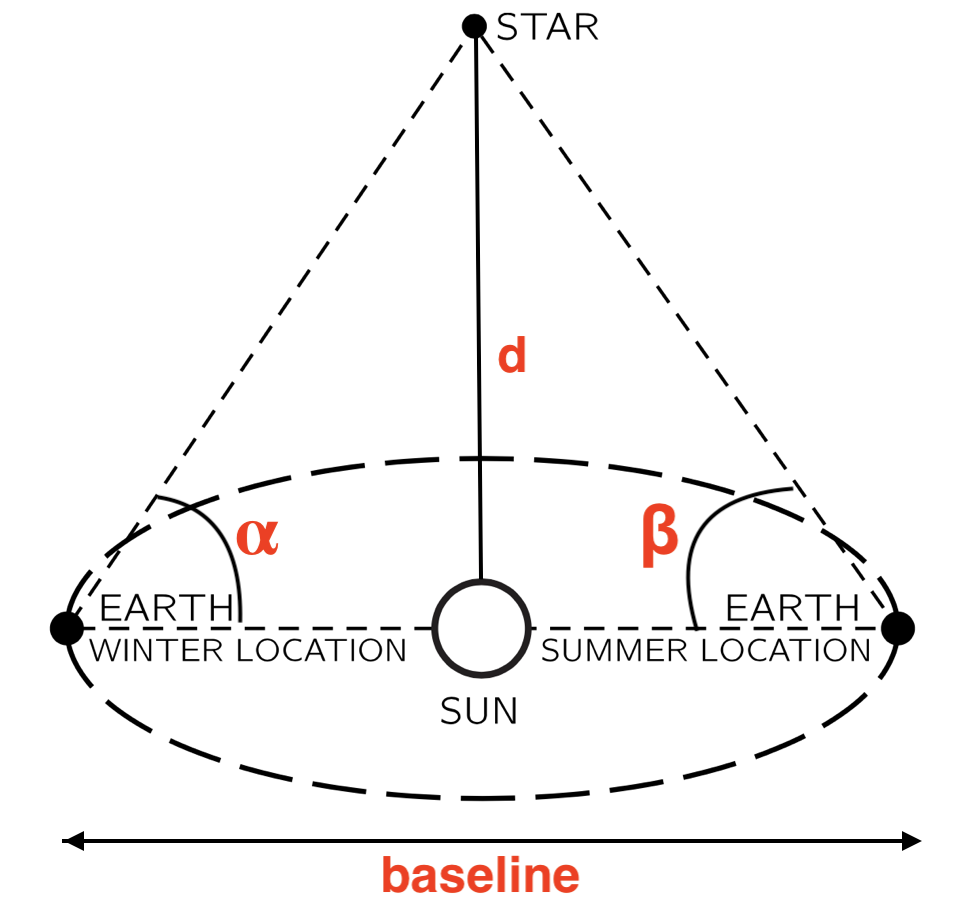
To find the 2 angles, we focus the telescope on the star, then wait for 6 months till the earth orbits to its opposite position to measure the angle again.
Now we have a triangle with 2 angles and one distance, it's the matter of basic math to find out the distance.
With this technique, we can measure stars within 400 light-years (or
Beyond 400 light years?
To measure stars further away, we have to use a different technique. Triangulation has reached its limit with 300 million km baseline.
By measuring stars within 400 light-years, astronomers have found a relationship between a star's brightness and how far it is. This is very intuitive: the closer we are to a lightbulb, the brighter it is.
Therefore, if we know how bright a star appears to us, we can estimate how far away it is using our recorded data between brightness and distance.
TL;DR
Triangulation for objects within 400 light years and brightness of light for stars beyond that.